ETFE Architectural Membrane & Film
- Transparency
- Lightweight
- Flexibility
- High Tensile Strength
- Thermal Performance
- Self-Cleaning
- Fire Resistance
Need Help?
Message Us






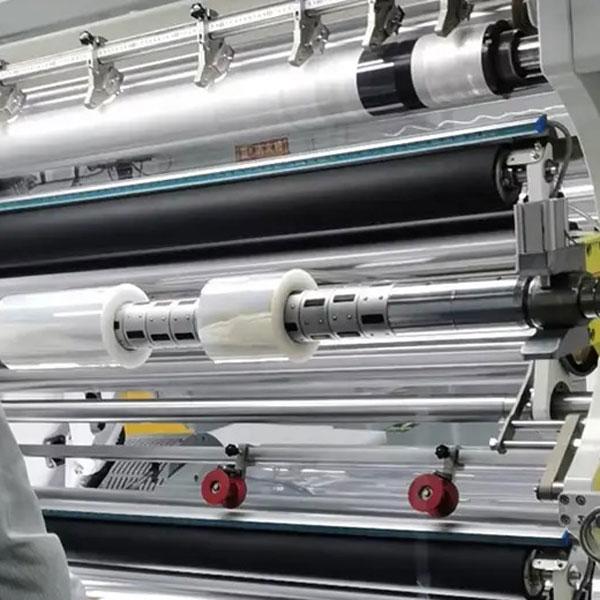
ETFE Membrane & Film Fabrication
The production process of ETFE membrane includes the following steps:
- Raw material preparation – Mix ethylene and tetrafluoroethylene in a certain proportion and process it into ETFE resin.
- Film extrusion – This is the core process of ETFE film production. The ETFE resin is heated, melted, and pushed into the die. In the die, the ETFE resin is extruded and cooled to form a flat film. The thickness of the film can be adjusted according to needs, usually between 0.1mm and 0.25mm.
- Film stretching – After cooling, the extruded film needs to be stretched to improve its mechanical properties and transparency.
- Film coating – In order to improve the weather resistance and chemical corrosion resistance of ETFE film, it is usually coated. Commonly used coating materials include fluorocarbon coating and silane coating.
- Film cutting – Cut the film to the required size.
- Inspection – Conduct quality inspection on the cut film to ensure that it meets the requirements.
ETFE Membrane & Film Structure

Single-Layer
A single layer of ETFE film is stretched to form a transparent membrane. It is often used in lightweight canopies, skylights, or atriums to provide basic protection against weather conditions.

Cushion System
ETFE cushions are pillow-like structures formed by sealing two layers of ETFE film and filling them with air or other gases. They are commonly used in large-scale roof and facade applications.

Foil System
By incorporating foil into ETFE film can enhance its thermal insulation capabilities. This can be useful in applications where temperature control or resistance to heat transfer is important.
ETFE Membrane & Film Applications

Architectural Roofs
ETFE membranes used in architectural applications are often in the form of inflated cushions or single-layer or multi-layer structures. The lightweight nature of ETFE membrane makes it suitable for creating transparent roofs and facades in buildings. The material allows natural light to penetrate while providing insulation and protection.

Agricultural Greenhouses
ETFE films for agricultural purposes are typically single-layer structures and the thicknesses range from 0.15 to 0.25 mm. They provide a controlled environment for plants. ETFE’s UV transparency allows for optimal sunlight penetration, promoting plant growth, while its durability ensures long-term performance in outdoor conditions.
Photovoltaic Applications
ETFE films used in solar panels can have thicknesses ranging from 50 to 300 microns (0.05 to 0.3 mm). As a protective layer for photovoltaic cells to enhance their performance and longevity. Its high light transmittance, resistance to the environment, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it suitable for this application.
ETFE Membrane & Film Videos
ETFE Film Manual Cutting
ETFE Architectural Membrane
ETFE Solar Panel Film
Contact Us

