Processing PEEK presents a unique set of challenges for manufacturers, stemming from its high processing temperatures, thermal degradation risks, and poor melt flow characteristics.
In this article, we will delve into the challenges associated with manufacturing PEEK products and explore the latest innovations in manufacturing techniques and technologies that address these obstacles.
Challenges in Fabricating PEEK
1. High Processing Temperatures
One of the primary challenges associated with PEEK is its high processing temperature requirement. PEEK typically needs to be heated to temperatures above 360°C (680°F) during molding, which can lead to increased energy consumption and wear and tear on processing equipment. Controlling and maintaining such high temperatures consistently can be demanding for manufacturers.
2. Thermal Degradation
PEEK is susceptible to thermal degradation if exposed to processing temperatures for extended periods. The risk of degradation can result in a decrease in mechanical properties and the generation of unwanted by-products. Striking a balance between achieving optimal processing temperatures and preventing thermal degradation is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the final product.
3. Poor Melt Flow Characteristics
PEEK exhibits relatively poor melt flow characteristics compared to other thermoplastics. Its high viscosity at processing temperatures can lead to challenges in achieving uniform mold filling, resulting in incomplete parts and uneven distribution of material. Improving the melt flow of PEEK without compromising its desirable properties is an ongoing concern for manufacturers.
Innovations in Manufacturing Techniques and Technologies
1. Advanced Processing Equipment
Manufacturers are investing in advanced processing equipment designed to handle the high temperatures required for PEEK. This includes specialized injection molding machines, extruders, and molds equipped with advanced temperature control systems to ensure precise and consistent processing conditions.
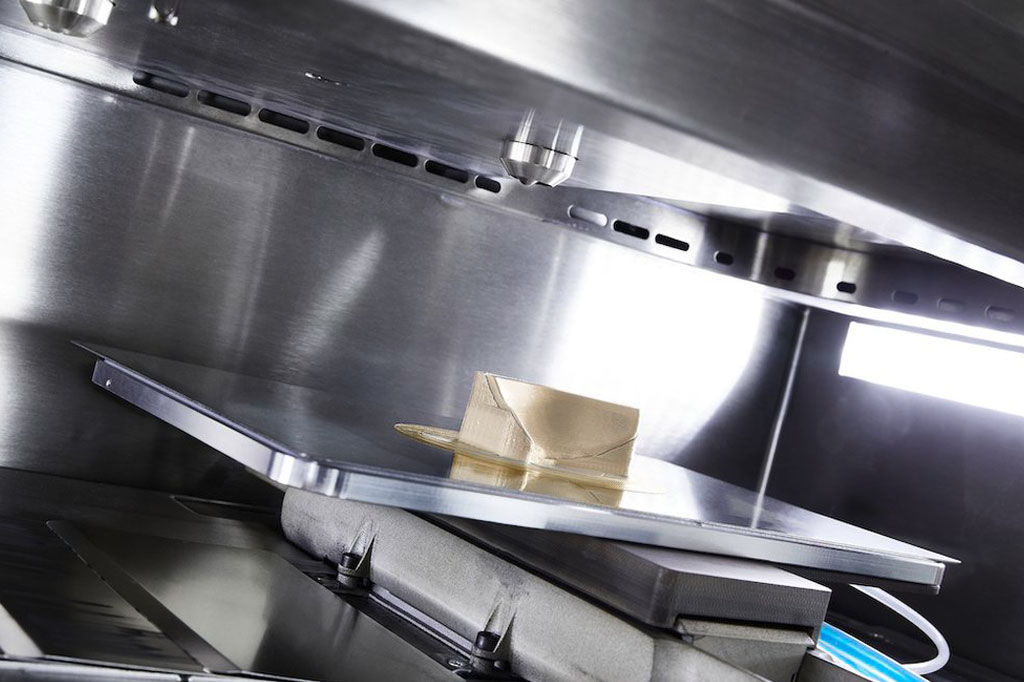
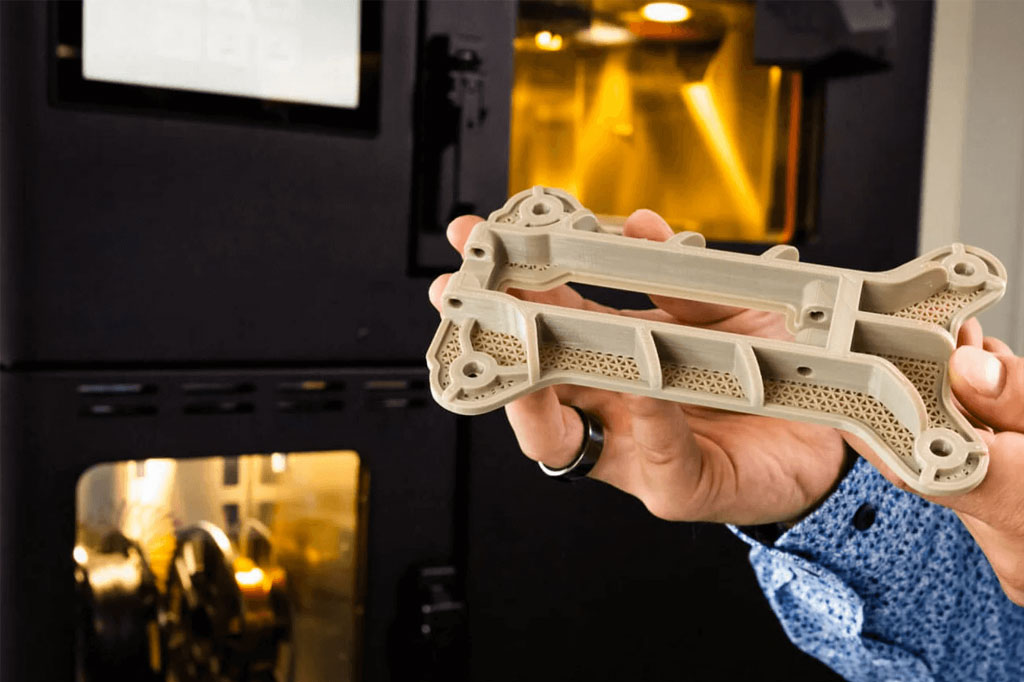
2. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
The advent of additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, has opened new possibilities for processing PEEK. Selective laser sintering (SLS) and fused filament fabrication (FFF) methods enable the production of complex PEEK components with reduced material waste.
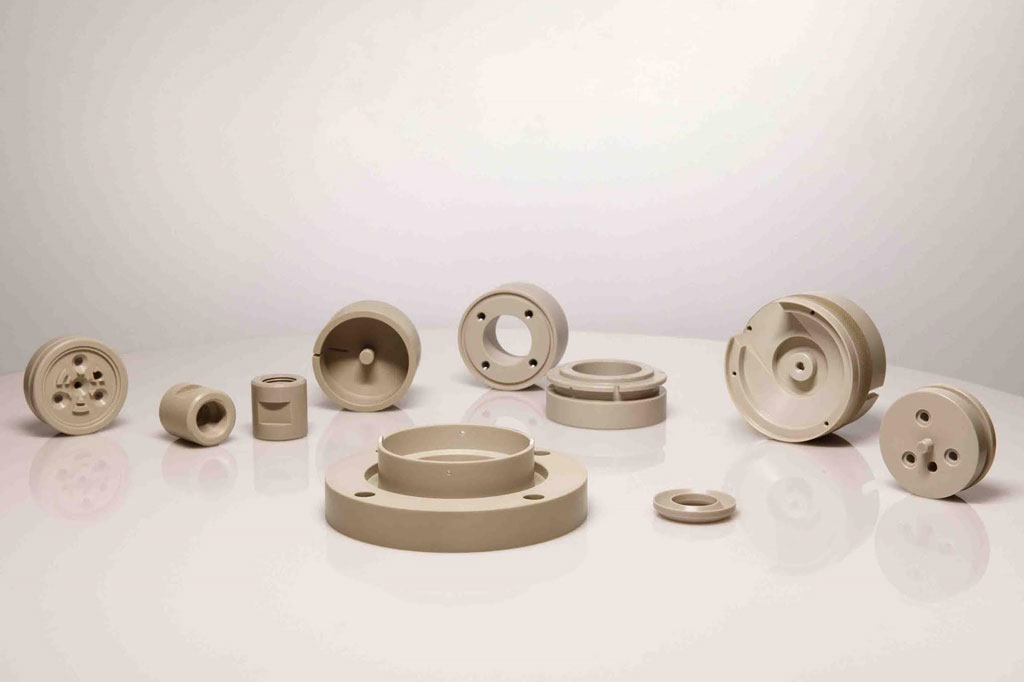
3. Reinforcement Technologies
Incorporating reinforcing materials, such as carbon fibers, into PEEK formulations has proven effective in addressing challenges related to poor melt flow and enhancing overall mechanical properties. Reinforcement technologies contribute to the development of PEEK composites, which offer improved strength, stiffness, and thermal stability.
4. Advanced Cooling Techniques
Efficient cooling is essential to prevent thermal degradation during PEEK processing. Innovative cooling techniques, such as active cooling systems and mold designs that optimize heat dissipation, contribute to maintaining uniform temperatures and minimizing the risk of thermal degradation.
Conclusion
From specialized processing equipment to additive manufacturing and reinforcement technologies, the evolving landscape of PEEK processing is paving the way for the broader utilization of this exceptional thermoplastic polymer across diverse industries.